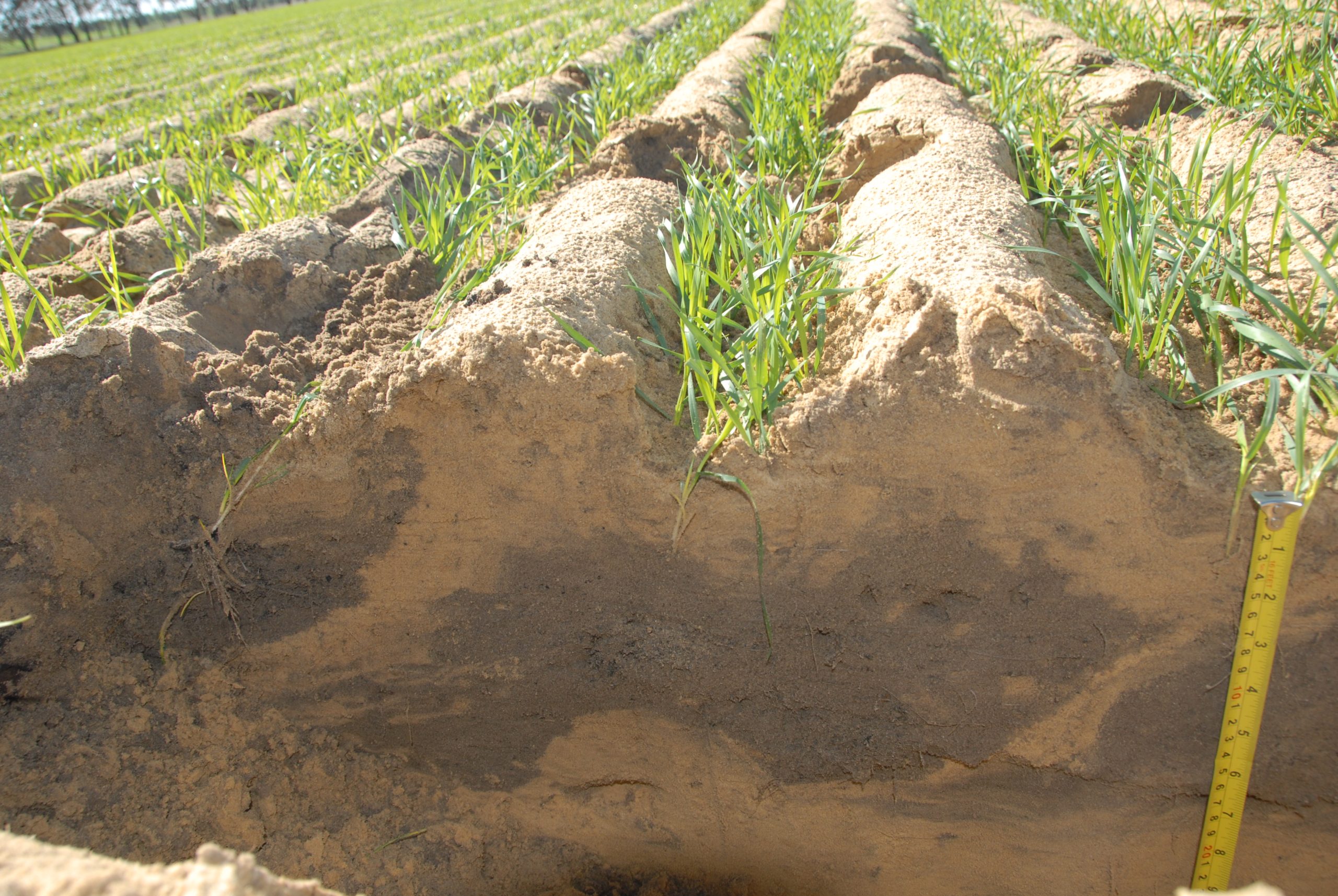
Soil is the lifeblood of agriculture. It’s the medium in which plants grow, providing them with essential nutrients.
But what happens when the soil becomes depleted or unbalanced? This is where soil amelioration comes into play.
Soil amelioration is a practice aimed at improving soil health. It involves various techniques to enhance soil structure, fertility, and overall productivity.
In this article, we delve into the concept of soil amelioration. We’ll explore its history, methods, and benefits.
Whether you’re a farmer, a gardener, or simply interested in sustainable agriculture, this guide will provide valuable insights. Let’s embark on this journey to understand and appreciate the importance of soil amelioration.

Understanding Soil Amelioration
Soil amelioration is a broad term. It encompasses various practices aimed at enhancing the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil.
The goal is to improve soil structure and fertility. This, in turn, boosts plant growth and yield.
Soil amelioration can involve adding organic matter like compost or manure. It can also include adjusting soil pH levels to optimize nutrient availability.
Moreover, soil amelioration practices can help increase water retention and drainage. They can also reduce soil erosion, promoting sustainable farming.
The History and Evolution of Soil Amelioration
Soil amelioration is not a new concept. It has been practiced for centuries, albeit in different forms.
Early farmers understood the importance of maintaining soil health. They used primitive methods like crop rotation and green manure to replenish soil nutrients.
Over time, these practices have evolved. Today, we have a better understanding of soil science and more sophisticated techniques for soil amelioration.
Soil Amelioration vs. Soil Amendments
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there’s a subtle difference between soil amelioration and soil amendments.
Soil amendments are materials added to the soil to improve its physical properties. They include compost, manure, and other organic matter.
Soil amelioration, on the other hand, is a broader concept. It includes the use of soil amendments but also encompasses other practices aimed at improving soil health. These can include adjusting pH levels, enhancing microbial activity, and managing soil compaction.
The Importance of Soil Fertility
Soil fertility is crucial for plant growth. It determines the amount and variety of nutrients available to plants.
Healthy, fertile soil is rich in organic matter. It has a balanced pH and a good structure that allows for proper water retention and drainage.
Soil fertility can be depleted over time due to various factors. These include erosion, overuse of chemical fertilizers, and poor farming practices.
Soil amelioration can help restore and maintain soil fertility. It can replenish lost nutrients and improve soil structure, promoting healthier plant growth.
Enhancing Soil Structure Through Amelioration
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles. It plays a significant role in determining the soil’s ability to retain water and nutrients.
Poor soil structure can hinder plant growth. It can lead to waterlogging or drought conditions, depending on the size and arrangement of soil particles.
Soil amelioration can improve soil structure. It can help create a more porous structure that allows for better water retention and nutrient availability.
Organic Matter and Soil Health
Organic matter is a key component of healthy soil. It provides nutrients and serves as a habitat for beneficial microorganisms.
Adding organic matter to the soil can improve its fertility. It can increase nutrient availability and enhance soil structure.
Soil amelioration often involves the addition of organic matter. This can be in the form of compost, manure, or green manure.
Practical Methods of Soil Amelioration
Soil amelioration involves various methods. These methods aim to improve soil health and fertility.
One common method is the addition of organic matter. This can be in the form of compost, manure, or green manure.
Another method is adjusting soil pH levels. This can be done through the addition of lime or sulfur, depending on whether the soil is too acidic or alkaline.
Adjusting Soil pH Levels for Optimal Growth
Soil pH is a critical factor in plant growth. It affects the availability of nutrients in the soil.
If the soil is too acidic or alkaline, certain nutrients may become unavailable to plants. This can hinder their growth and development.
Soil amelioration can help adjust soil pH levels. This can be done through the addition of lime to raise pH or sulfur to lower it.
Common Soil Ameliorants and Their Uses
There are various soil ameliorants that can be used in soil amelioration. These include organic matter, lime, sulfur, and gypsum.
Organic matter, such as compost and manure, can improve soil structure and nutrient availability. Lime and sulfur can adjust soil pH levels.
Gypsum can improve soil structure, especially in clay soils. It can help break up compacted soil and improve water infiltration.
- Organic matter: Improves soil structure and nutrient availability
- Lime: Raises soil pH
- Sulfur: Lowers soil pH
- Gypsum: Improves soil structure in clay soils
Benefits of Soil Amelioration
Soil amelioration offers numerous benefits. It can significantly improve soil health and fertility.
By enhancing soil structure, it can improve water retention and drainage. This can lead to healthier plant growth and higher crop yields.
Moreover, soil amelioration can reduce soil erosion. It can help maintain soil health and productivity over the long term.
Sustainable Farming and Environmental Benefits
Soil amelioration also plays a crucial role in sustainable farming. It can reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
By improving soil health, it can enhance the sustainability of farming practices. This can lead to more resilient and productive agricultural systems.
Furthermore, soil amelioration can have significant environmental benefits. It can help sequester carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation. It can also enhance biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Conclusion: The Future of Soil Amelioration
Soil amelioration is not just a practice of the past, but a key strategy for the future. As we face challenges like climate change and food security, its importance cannot be overstated.
Innovations in technology and farming practices are continually enhancing soil amelioration methods. From precision agriculture to nanotechnology, the future of soil amelioration is promising.
In conclusion, soil amelioration is a vital tool for sustainable agriculture. By understanding and implementing effective soil amelioration practices, we can ensure healthier soils, higher crop yields, and a more sustainable future for all.